A
What happened
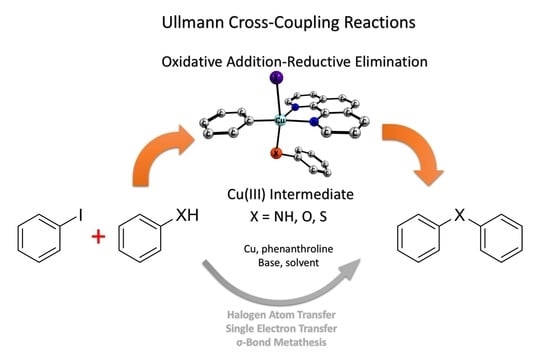
The study investigates the redox behavior of copper in Ullmann-type coupling reactions, focusing on the interaction between a Cu(I) complex and an electron-poor aryl iodide. This interaction leads to the formation of a Cu(III)−aryl complex, which subsequently undergoes reductive elimination to create a C(sp2)−CF3 bond. Through a combination of experimental and theoretical approaches, the research reveals a redox cycle involving Cu(I), Cu(III), and Cu(II) species. Temperature control was utilized to interrupt this cycle, allowing for detailed spectroscopic analysis of copper's reactivity. These findings challenge traditional mechanistic views and provide new perspectives on copper-catalyzed coupling reactions, highlighting the intricate behavior of copper species in catalysis.
★
Key insights
-
1
Copper's Role in Catalysis
The study enhances understanding of copper's behavior in catalytic processes.
-
2
Redox Cycle Discovery
A new redox cycle involving Cu(I) and Cu(III) species was identified.
Takeaways
This research provides significant insights into the mechanisms of copper-catalyzed reactions.